Plant maintenance shutdowns and turnarounds are the most expensive of all types of maintenance. Because of their high impact to plant production, as well as the high cost of parts and equipment, plant shutdowns require a dedicated shutdown team. This specialized team requires a strict process to follow, and the backbone of that process is the 5 Phases of Shutdown Maintenance.
Note: This post may contain affiliate links. Please read our disclosure policy for more information.
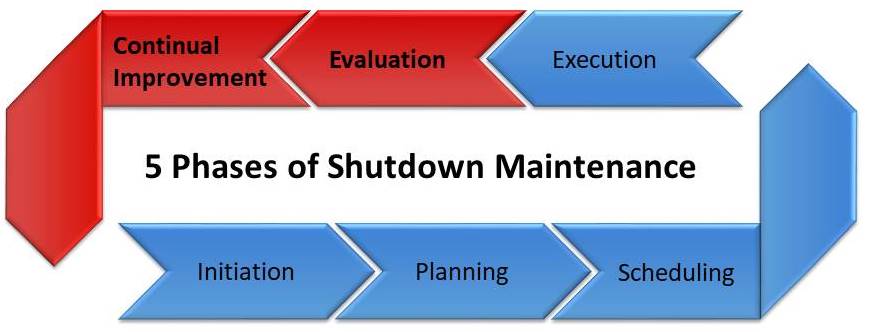
What are the 5 Phases of Shutdown Maintenance?
A Plant Maintenance Shutdown is more similar in a lot of ways to a project, instead of regular maintenance. You can consider it to be a Shutdown Project, with 5 distinct phases.
- Initiation
- Planning
- Scheduling
- Execution
- Evaluation
Phase 1: Shutdown Initiation
A shutdown maintenance event must be carefully defined early in the piece to align with the business goals of the site. Shutdown objectives must be well defined, and preferably measurable. These are effectively the KPI’s for the shutdown, which are often standardized across the organization. Some examples of shutdown objectives are:
- Zero harm to shutdown workforce
- Emergent work to be restricted to 10% of planned work
- Shutdown costs to be within budgeted costs
- Shutdown overrun to be less than 5%
Some key issues which must be addressed during the shutdown initiation phase are:
- Shutdown date
- Shutdown duration
- Overall Shutdown budget
- Shutdown objectives
- List of equipment to be taken offline
- Scope of work for equipment taken offline
- New equipment to be installed
- Equipment to be modified
- Who will manage the shutdown
- Who will execute the shutdown
- Key dates for each shutdown phase
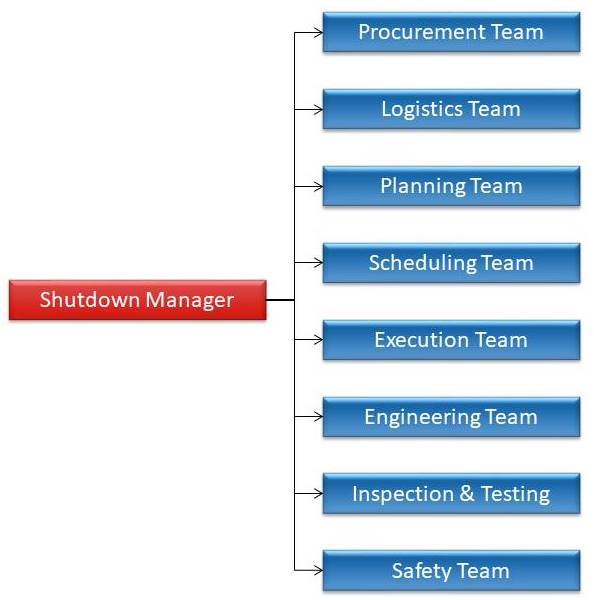
The Shutdown Team
The shutdown team must be identified and assembled as soon as possible after the previous shutdown. Normally the core team will consist of the following. Depending on the size of the plant, some roles may be done by the same person.
- Shutdown Manager
- Planner(s)
- Scheduler(s)
- Shutdown Coordinator
The Shutdown Committee
In addition to the shutdown team, a shutdown committee should also be appointed. The committee will meet regularly to make decisions on key shutdown issues. The shutdown committee would normally consist of the following:
- Maintenance Manager / Superintendent
- Processing Manager / Superintendent
- Senior Maintenance Supervisor(s) from different disciplines
- Senior Materials Management person
- Reliability Engineering person
During the shutdown initiation stage, the shutdown planning process must be documented. There should be a standard template developed with tasks and milestones scheduled for each shutdown phase.
Phase 2: Shutdown Planning
The Planning phase is all about identifying the shutdown work scope, then identifying parts, labor, equipment and other resources required to carry out the shutdown. The output of the planning phase is a set of comprehensive shutdown work packs, assurance that everything is available to carry out the work.
It is imperative that a specialist planning team is assigned to this phase. That is to say, do not try to use the routine planners to carry out the shutdown planning ‘in their spare time’. The nature of shutdown planning requires laser focus, and the planners must not be distracted by other routine activities.
Shutdown Scope
Prior to the identification of parts, labor, equipment and resources it is necessary to define the shutdown work scope. This will normally involve high level meetings and involve Processing, Maintenance and Engineering departments.
After the high level scope is determined the CMMS will normally be used to find other jobs to be included in the scope. This will identify PdM and corrective maintenance requirements. Note that a crucial step in the Planning phase is to identify a cut-off date for accepting new work.
Parts
Early in the Planning phase it is necessary to identify long lead time items. Some of these may take many months to procure, or even years. This will often involve design steps, and will almost certainly involve some kind of tender process.
Long lead time items are a complex part of the planning process, as they will often span across several different departments. Procurement, Maintenance, Processing, Engineering and even Contract Specialists will all have stake in organizing necessary parts. Thus careful coordination is critical to ensure reliable management of materials.
All required parts must be sourced and then delivered to a central shutdown staging area. It is important to have a dedicated and secure area to stage all shutdown components. It is equally important to have a dedicated materials coordinator to manage the delivery and storage of all shutdown components.
Labor
The size of the additional labor requirements must be identified and organized. Often this will require a tender process, or there may be specific contracts already set in place. Contractor request documentation is to be submitted, and Service Orders initiated.
Equipment
Specialized equipment is a normal requirement for shutdowns and turnarounds. Cleaning equipment, machining equipment, heavy lifting equipment, hand tools, specialist tooling. The list goes on when it comes to equipment requirements. It is important that all equipment requirements are identified for all shutdown jobs as early as possible, as some of these may require a lengthy process to properly organize. Usually it will be more cost effective to rent equipment rather than outright purchase.

Other Resources
Often specialist resources are required. The logistics of executing a large turnaround is complex, and requires careful planning of a wide range of resources. For example: messing facilities, toilets, transportation, communication and security. These must all be identified and organized during the planning phase of the shutdown.
Phase 3: Shutdown Scheduling
Similar to the shutdown planning phase, it is important that a dedicated shutdown scheduling team is appointed. The required skill set for a shutdown scheduler is different than for a shutdown planner, thus it is better to have separate planners and schedulers.
The core task of the Shutdown Scheduler is to activities. Other core activities during the scheduling phase are:
- Ensure the full scope of work can be carried out within the allocated time.
- Define the timing requirements for all parts, labor, equipment, and other resources for execution of shutdown maintenance activities.
- Define the critical path activities for the shutdown.
- Sequence the work to optimize the use of all shutdown resources, often referred to as resource leveling.
- Identify shutdown job priorities, and utilize float to schedule shutdown work in accordance with priorities.
During the scheduling phase many meetings are necessary involving all major stakeholders of the shutdown. High level meetings are required to discuss overall shutdown scope and sequencing. Low level meetings are required to determine detailed job sequencing. And logistics meetings are required to organize timely delivery and staging of parts and equipment.
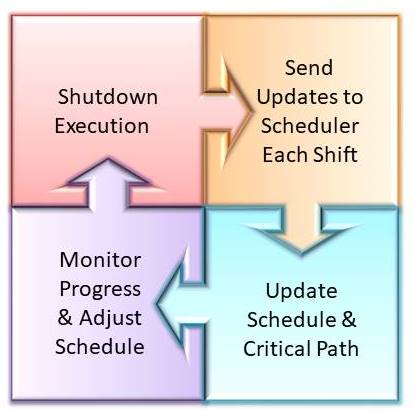
Phase 4: Shutdown Execution
The Maintenance Supervisors are responsible for driving the shutdown execution. They use the work packs produced by the shutdown planner in conjunction with the schedule produced by the Shutdown Scheduler to complete each task at the allocated time.
Shutdown supervisors must update progress regularly to the Shutdown Scheduler. This would normally be done once per shift using schedule update sheets. The Shutdown Scheduler is then responsible for monitoring the overall progress of the shutdown. In particular the Shutdown Scheduler must monitor the critical path. If there are any interferences to the timely completion of the critical path activities must be identified as early as possible, and adjustments made. This may be to change scope or even remove jobs from the schedule.
Phase 5: Shutdown Evaluation
Shutdown Evaluation involves steps to use a process of assessment and continual improvement to ensure that future shutdowns and turnarounds can be improved by acting on lessons learnt. It is of vital importance that a post shutdown analysis is carried out soon after the completion of the shutdown.
A common way to collect feedback is to distribute a post-shutdown questionnaire to participants of the shutdown execution. These are completed and returned to the shutdown planning team for evaluation. The questionnaire will cover issues, shutdown evaluation, and opportunities for improvement. These should be compiled into a formal post shutdown report.
Another common way to collect feedback is via a post-shutdown meeting. This must be done immediately after completion of the shutdown before relevant personnel are demobilized, thus it may be more difficult to accomplish than a questionnaire.
Lessons learnt register is a valuable way to capture all lessons learned from a shutdown. This can also serve as a useful tool to assign accountability to individuals to act upon lessons learned, and to ensure the success of future shutdowns and turnarounds.
The Key to Shutdown Maintenance Success
The key to successful shutdown project is to have a robust shutdown process in place. The shutdown maintenance process must be well documented, and be built on a solid foundation. And that foundation is the 5 phases of shutdown maintenance. Follow these closely and you are well on the way to a successful shutdown.
Learn More about Shutdown Maintenance
There are no secrets to success. It is the result of preparation, hard work, and learning from failure.
Colin Powell
Learning from text books is one key step to enduring success. Here is some recommended reading to help you in your pursuit of excellence.
Would you like a free copy of 7 Steps to Become a KPI Ninja?
Not sure how to set up your Maintenance KPI’s? We have created the 7 Steps to Become a KPI Ninja guide to help you build, analyse and improve your KPI’s. It contains details of all the best metrics to measure, and how to interpret them. And we want you to have it for FREE.







